Characteristics of Debris Flow
- Debris flow is a combination of fast moving water and a great volume of sediment and debris that surges down slope with erosive energy and tremendous force.
- A debris flow can be divided into two layers: a fast moving upper layer and a relatively slow moving lower layer.
- Debris flow velocity varies with sediment size, water and clay content and valley-side slope. Velocities of granular flows range from 3 to 10 m/s, and velocities of mud flows range from 2 to 20 m/s.
- The front, or 'head' of a debris-flow surge often contains an abundance of coarse material such as boulders and logs. The following flow contains a higher percentage of sand, silt and clay.
- Gravels are deposited by debris flows which deform underlying sands.
- The debris flow fan is built up because the wide river width and flat valley slope at the end of river which decreases the debris flows velocity. Hence, debris flow usually drops its loads here.

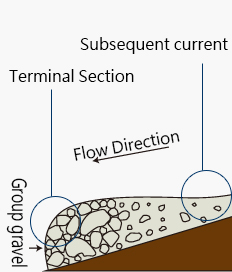
Larger grain floats within a matrix of smaller stones

Causes of Debris Flow
- Abundant sources: large amounts of loose debris, including fine (clay, silt and sand) and coarse (gravel, cobbles and boulders) materials.
- Sufficient water: water acts as a lubricant, reducing friction among debris and allowing solid materials to flow.
- Steep slopes: in areas of quite steep slopes where lead debris to transport and flow down with lower friction.
 Descriptions
DescriptionsDebris flows are triggered by amount of debris flow sources from upstream area, quite steep slopes and large volumes of water. Near unstable mountain slopes, weathered rock, sand and soil accumulate in valleys or foothills by slide falls, landslides and rock falls. If those debris sources experience heavy rain one day, water will difficult to drainage from the heavy load of rock materials. In the state of high undrained loading water, the top debris sources become heavy and enhance debris flow mobility which often end up in devastating debris flow hazards.
Significant Signs Prior to A Debris Flow
Debris flows may happen when the three main causes (sufficient water, debris sources and steep slopes) exist in the same time. Here are the cause reasons and signs before the debris flow:
|
The indication of the occurrence of debris flow
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Time of the indication occurrence
|
Indication
|
Cause
|
|||
|
●
幾小時前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
一小時前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
幾分鐘前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
發生土石流發生可能性高
|
1.Landslide or debris flow occur nearby.(Visual) | Because the slope and the geology nearby have been in an unstable state. |
|
●
幾小時前發生土石流有發生可能
|
●
一小時前發生土石流有發生可能
|
●
幾分鐘前前發生土石流有發生可能
|
●
發生土石流有發生可能
|
2.The water flow of the torrent increases in a sudden.(Visual) | might be torrential rain at upstream area. |
|
●
幾小時前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
一小時前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
幾分鐘前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
發生土石流發生可能性高
|
3.Unusual sounds of mountains.(Hearing) | The landslide or debris flow might have occurred at upstream area. |
|
●
|
●
一小時前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
幾分鐘前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
發生土石流發生可能性高
|
4.The water flow of the torrent decreases sharply.(Visual) | The torrent upstream might have been blocked by the debris. |
|
●
|
●
一小時前發生土石流有發生可能
|
●
幾分鐘前發生土石流有發生可能
|
●
發生土石流有發生可能
|
5.There is driftwood in the torrent.(Visual) | The landslide or river-bank erosion might have occurred at upstream area. |
|
|
●
一小時前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
幾分鐘前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
發生土石流發生可能性高
|
The river water is abnormally turbid.(Visual) | The landslide or river-bank erosion might have occurred at upstream area. |
|
|
●
一小時前發生土石流有發生可能
|
●
幾分鐘前發生土石流有發生可能
|
●
發生土石流有發生可能
|
7.Friction sound of stones in the river. (Hearing) | Because the water flow of the river increases. |
|
|
●
一小時前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
幾分鐘前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
發生土石流發生可能性高
|
8.Stinky smell of humus soil. (Olfactory) | The smell comes from the fallen trees caused by landslides. |
|
|
●
一小時前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
幾分鐘前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
發生土石流發生可能性高
|
9.Cracking sound of trees. (Hearing) | flow might happened upstream and cause the cracking sound. |
|
|
●
一小時前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
幾分鐘前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
發生土石流發生可能性高
|
10.Abnormal actions of animals.(Visual) | Animal sensory is more sensitive than human's, that means animals might be able to feel the abnormal phenomenon of nature which human cannot be aware of. |
|
|
|
●
幾分鐘前發生土石流發生可能性高
|
●
發生土石流發生可能性高
|
11.Ground vibrating.(Tactile) | The vibration comes from the tumbling of debris flow. |
|
|
|
●
|
●
發生土石流必定發生
|
12.At upstream area there is weird noise which sounds like “Go”, and fire flame or thunder lightning. (Hearing and Visual) | giant rocks strike each other while the debris flow occurs. |
|
Few hours ago
|
An hour ago
|
Few minutes ago
|
the debris flow occurs
|
Marking:
Must ● Highly possible ● Possible ● |
|
Classification of debris flows
The types of debris flows are classified according to forming causes, topography, debris material, debris sources, flow types, triggering factors, movement mechanisms, developmental stages and etc.
| Classification | Category | References |
|---|---|---|
| Causes of debris flow | Natural factors and human factors | ZHAN,QIAN-DENG(2000) |
| Landslide range of debris flow | Large-scale, source-induced, small-scale, deposition-mobility of river bank | Takahashi(1977) |
| Flow types | Sliding, collapsing, gully erosion, hillslope erosion | JHOU,BI-FAN(1980) |
| Hazard factors | Intensive rainfall, snowmelt, intensive rainfall with snowmelt, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions | Hiroshi Ikeya(1980) |
| Developmental stages | Initial stage, mature stage, recession stage, stationary stage | CHEN,GUANG-XI(1983) |
| Causing factors | Spontaneous, triggered or induced by landslide, heavy rain, etc. | LYU,RU-REN(1988) |
| Topography | Valley-typed and Hillslope debris flow | JHOU,BI-FAN,etc.(1991) |
| Contributing factors | Geological formations, hydrogeological factors | JHOU,BI-FAN(1991) |
| Movement conditions | Hydraulic factors, gravity, dynamic factors | WU,JIAN-MIN(1991) |
| Debris flows occurrence | Hillslope liquefaction, failure of landslide dam, unstable deposition accumulated on river bank | Takahashi(1991) |
| Debris sources | Granular flow, mudflow, normal debris flow | Manual of Soil and Water Conservation(1992) |
More Debris Flow Information